Tommy J Housman
December 29th 2024
MAGA Civil War
At the heart of this dispute lay the question of immigration, specifically the H-1B visa program for skilled foreign workers. Traditional MAGA, with its “America First” ethos and focus on limiting immigration, viewed the program as a threat to American jobs and wages. The DOGE faction, however, comprising tech billionaires and entrepreneurs, saw the H-1B program as essential for attracting top talent and maintaining American competitiveness in the global tech industry.
The battle lines were drawn on December 22nd when Trump announced Sriram Krishnan, an Indian-born tech entrepreneur, as his senior policy advisor on artificial intelligence. This appointment triggered an immediate backlash from prominent MAGA figures, most notably Laura Loomer, a staunch Trump supporter and vocal critic of immigration. Loomer, who had previously been sidelined from Trump’s inner circle due to her inflammatory rhetoric, took to X to denounce Krishnan’s appointment, highlighting his support for expanding the H-1B visa program.
“These jobs,” Loomer declared, “should be given to American STEM students.” She further accused the DOGE faction of enriching themselves at the expense of MAGA loyalists, stating, “I feel like many of them are trying to get into Trump’s admin[istration] to enrich themselves and get contracts at [the] D[epartment] O[f] D[efense]. This is not America First Policy.”
Loomer’s accusations struck a nerve within the traditional MAGA base, who felt increasingly marginalized by the influx of tech billionaires into Trump’s orbit. The perception that DOGE was prioritizing corporate interests over the concerns of working-class Americans fueled resentment and suspicion. When David Sacks, another tech entrepreneur and Trump appointee, defended Krishnan, Loomer responded with a series of racially charged posts, claiming, “Our country was built by white Europeans, actually. Not third-world invaders from India.”
Elon Musk, a self-proclaimed “free speech absolutist,” initially remained silent on the brewing conflict. However, on Christmas Day, he weighed in with a forceful defense of skilled immigration, arguing that the U.S. needs to double its engineering workforce to maintain its global dominance. “The number of people who are super talented engineers AND super motivated in the USA is far too low,” Musk tweeted. “Think of this like a pro sports team: if you want your TEAM to win the championship, you need to recruit top talent wherever they may be. That enables the whole TEAM to win.”
Musk’s intervention, rather than calming the storm, only served to intensify the conflict. Traditional MAGA supporters pushed back against his characterization of American workers as lacking in talent and motivation. Elon Musk posted, “Investing in Americans is actually hard. Really hard. It costs money and time and effort to make a person productive. It’s a short term net loss. It’s much easier to bring in skilled workers who might not do quite a good a job [sic], but will work for a fraction of the cost and be happy just to be here.”
Loomer, undeterred by Musk’s stature, continued her attacks, labeling him a “stage 5 clinger” who had overstayed his welcome in Trump’s inner circle. She further accused Musk of using his wealth to manipulate immigration policy for personal gain, stating, “We all know you only donated your money so you could influence immigration policy and protect your buddy Xi JinPing.”
The conflict reached a boiling point on December 26th when Vivek Ramaswamy, posted a scathing critique of American culture, suggesting that its emphasis on mediocrity over excellence was to blame for the lack of qualified American engineers. “American culture has venerated mediocrity over excellence for way too long,” Ramaswamy wrote. “A culture that celebrates the prom queen over the math olympiad champ, or the jock over the valedictorian, will not produce the best engineers.” He further called for a cultural shift that prioritizes academic achievement over social pursuits, advocating for “more math tutoring, fewer sleepovers. More weekend science competitions, fewer Saturday morning cartoons. More books, less TV.”
Ramaswamy’s pronouncements ignited a firestorm of criticism from both traditional MAGA supporters and establishment Republicans. Nikki Haley, a former South Carolina governor and Trump rival, retorted, “There is nothing wrong with American workers or American culture. All you have to do is look at the border and see how many want what we have. We should be investing and prioritizing in Americans, not foreign workers.”
Loomer, seizing on the opportunity, accused DOGE of redirecting government spending towards “the pet projects of tech bro billionaires” under the guise of “cutting spending.” Other right-wing commentators echoed her concerns, questioning the sincerity of DOGE’s commitment to reducing government waste and accusing them of favoring corporate interests over the needs of working-class Americans.
As the conflict escalated, Musk took increasingly drastic measures to silence his critics. When Loomer continued her attacks, Musk appeared to limit her access to X, prompting accusations of censorship and hypocrisy from the MAGA base. “I have always been America First and a die hard supporter of President Trump and I believe that promises made should be promises kept,” Loomer declared. “Now, as one of Trump’s biggest supporters, I’m having my free speech silenced by a tech billionaire for simply questioning the tech oligarchy.”
The irony of a self-proclaimed “free speech absolutist” censoring dissenting voices did not escape the attention of Loomer and other MAGA supporters.
By the end of the week, the MAGA civil war had spilled over from X into the wider media landscape. Steve Bannon, a key Trump ally and a central figure in the MAGA movement, took to his own platform to denounce Musk’s “true colors” and demand the elimination of the H-1B visa program. Jack Posobiec, another influential right-wing figure, tweeted, “Today was the day we found out who is getting rich by screwing over the American worker.”
The ideological clash within the MAGA movement highlights all the societal debate voiced throughout the 2024 election over immigration, education, and workforce development in the United States. As automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and technological advancements reshape the labor market, questions about immigration, the value of higher education, and alternative career paths become increasingly urgent.
The Importance of Immigration to the U.S.
Immigrants have been a cornerstone of the United States’ economic success, contributing significantly to industries ranging from technology and healthcare to agriculture and manufacturing. Their importance cannot be overstated, especially at a time when the U.S. faces critical labor shortages and increasing global competition.
According to the National Immigration Forum, immigrants make up nearly 17% of the U.S. labor force, despite accounting for approximately 14% of the population. In 2021, immigrant-led households contributed over $330 billion in federal income taxes and $161 billion in state and local taxes, underscoring their pivotal role in supporting public services such as education and healthcare.
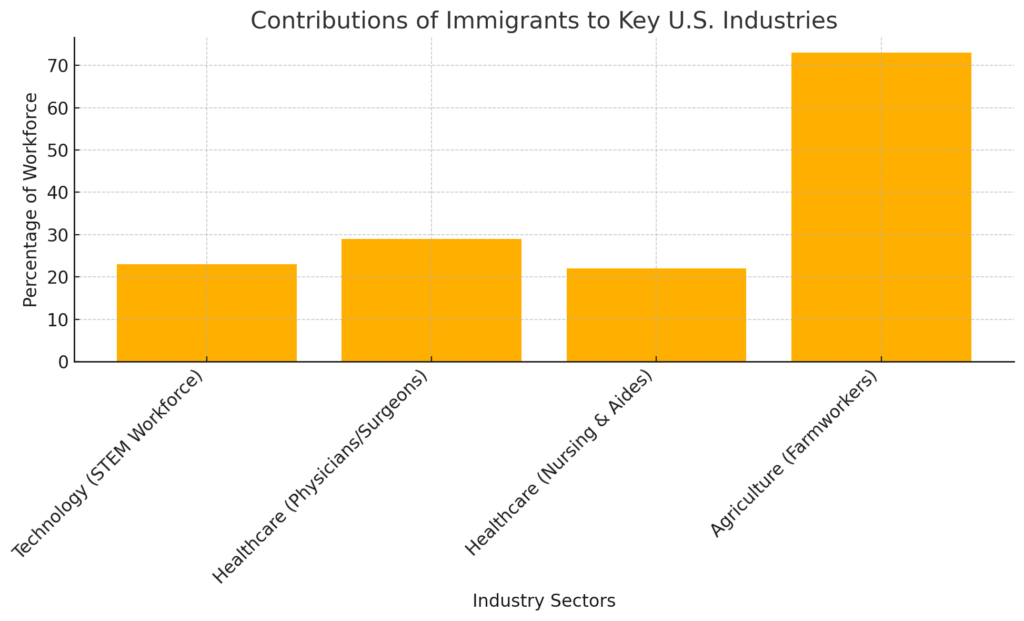
Beyond these contributions, immigrants are also key drivers of population growth in a country where the birth rate has fallen to 1.6 children per woman, far below the replacement rate of 2.1. This demographic shift highlights the growing reliance on immigration to sustain economic growth, support aging populations, and fund Social Security and Medicare programs.
Despite their contributions, immigrants face barriers such as restrictive visa policies and public misperceptions. Programs like the H-1B visa, which enables skilled workers to fill labor gaps, are often targets of political controversy. Yet, these policies ignore the reality: immigrants are not taking jobs away from Americans but filling critical gaps in sectors struggling to find qualified workers.
The long-term economic benefits of immigrant inclusion extend beyond individual industries. According to a study by the Center for American Progress, a pathway to citizenship for undocumented immigrants could boost U.S. GDP by $1.5 trillion over a decade, create hundreds of thousands of jobs, and increase wages for all workers. These findings emphasize that a welcoming immigration policy is not just morally sound but economically strategic.
Education
I did not see myself agreeing with these two this week, but here we are, Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy raise a compelling argument: over the past four decades, the United States has downplayed the value of higher education and specialized training for many young people, while other nations have made significant investments in secondary and post-secondary education. This divergence has left the U.S. grappling with a critical shortage of skilled workers, particularly in technology, healthcare, and other high-demand industries.
Beginning in the late 20th century, a growing narrative in the U.S. questioned the necessity of college education. Advocates of alternative paths argued that higher education was becoming prohibitively expensive and that lucrative careers in the trades offered a viable alternative. While this argument had merit, it overlooked the broader global trends. Many countries, particularly in Europe and Asia, were simultaneously doubling down on education, emphasizing STEM fields and healthcare training to meet future workforce demands. Countries like Germany expanded robust vocational training programs, while nations like China and India invested heavily in engineering and medical education.
Meanwhile, the U.S. faced declining enrollment rates in higher education. Undergraduate enrollment fell by 8% between 2019 and 2022, reflecting disillusionment with traditional education models during the COVID-19 pandemic, soaring tuition costs, and concerns about student debt. As a result, the talent pipeline for critical industries such as technology, engineering, and healthcare has thinned considerably. In 2023, the American Association of Colleges of Nursing reported that nursing schools were turning away tens of thousands of qualified applicants due to faculty shortages and budget constraints, exacerbating the nationwide nursing shortage.
Employment outcomes of college graduates compared to non-graduates highlight the economic advantages of higher education. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), in 2023, individuals aged 25 and over with a bachelor’s degree earned a median weekly wage of $1,493 and had an unemployment rate of just 2.2%. In contrast, those with only a high school diploma earned a median weekly wage of $899, with an unemployment rate of 3.9%. However, underemployment remains a significant issue; as of 2021, 41% of college graduates aged 22 to 27 worked in jobs that did not require a college degree.
The U.S. faces a widening skills gap, especially in industries that demand advanced technical expertise. The tech sector is perhaps the most visible example. While the demand for software engineers, data scientists, and AI specialists continues to skyrocket, the domestic supply of qualified candidates has not kept pace. According to the National Science Foundation, only about 10% of U.S. bachelor’s degrees are awarded in engineering, compared to 33% in China. This disparity is even starker in graduate-level education, where international students often outnumber domestic students in U.S. engineering and computer science programs.
Healthcare presents another glaring challenge. The U.S. faces a projected shortage of up to 124,000 physicians by 2034, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges. Similarly, the American Nurses Association estimates that the demand for registered nurses will outstrip supply by over 500,000 by 2030. These shortages strain healthcare systems, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
The skills gap is not confined to technology and healthcare. Advanced manufacturing, renewable energy, and infrastructure sectors are also experiencing a dearth of qualified workers. For example, the Biden administration’s push for clean energy initiatives has highlighted the need for skilled technicians to install and maintain solar panels, wind turbines, and EV charging networks. These industries require a workforce with specialized technical training, yet the U.S. educational system has not adequately addressed these needs.
The rising cost of college, coupled with soaring student debt, has created a significant barrier for many Americans, particularly those from low-income backgrounds. The debate over student loan forgiveness, which the Supreme Court appears poised to block, further highlights the financial burden that higher education places on individuals and families. As college becomes increasingly unaffordable, enrollment continues to decline. This trend, fueled by cost concerns, disillusionment with traditional education models, and questions about the value of a college degree, has far-reaching implications for the U.S. economy and society.
Countries that have prioritized education and workforce development offer valuable lessons, especially those that provide free or low-cost education, ensuring equitable access to skills development and advanced training. These nations have created systems that not only produce highly skilled workforces but also alleviate financial barriers that can limit educational attainment. Examples include:
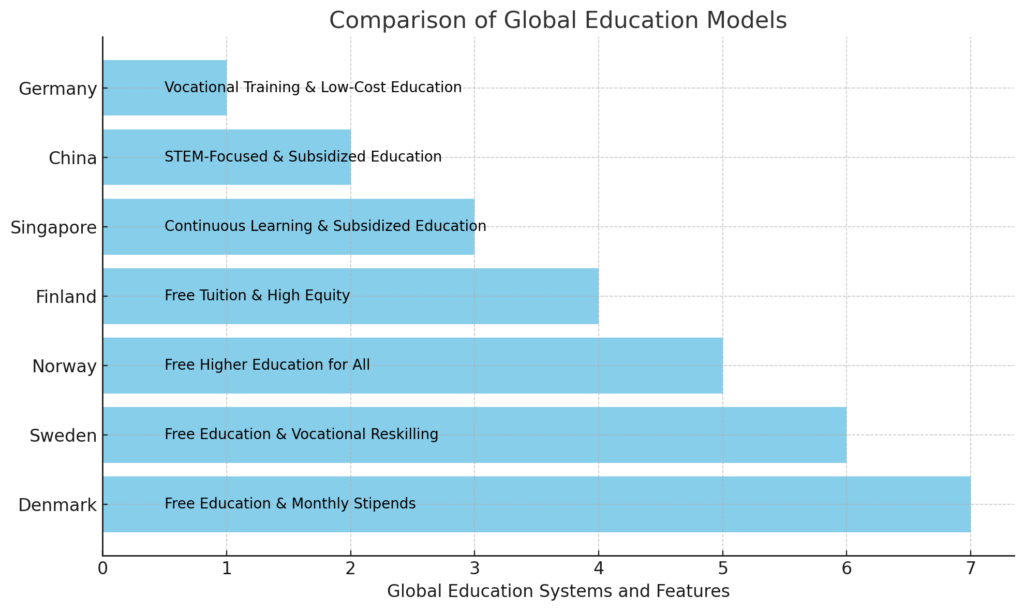
These countries have cultivated talent pipelines that prepare their populations for current and future economic challenges. These models highlight how the United States could benefit from reducing the cost of education while tailoring programs to address critical labor shortages in technology, healthcare, and other industries.
Policymakers and educational institutions must balance making higher education more accessible and promoting alternative pathways like apprenticeships and certifications in high-demand fields. Public and private sectors need to collaborate to:
1 Invest in STEM Education: Enhance funding for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics at all levels of schooling.
2 Expand Healthcare Training Programs: Address bottlenecks in medical and nursing education by increasing faculty capacity and resources.
3 Promote Lifelong Learning: Develop reskilling programs to ensure that current workers can transition into emerging industries.
While the U.S. remains a global leader in innovation, maintaining this status will require a renewed commitment to cultivating a skilled and educated workforce. The evolving labor market adds another layer of complexity to this discussion. A report from the McKinsey Global Institute predicts that by 2030, 30-50% of tasks currently performed in the U.S. economy could be automated. This shift is expected to disproportionately affect roles in office support, customer service, and food service while creating opportunities in healthcare and STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields. The integration of AI and automation promises increased productivity but also introduces challenges, including potential job displacement and the urgent need for workforce reskilling.
The implications are profound: the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that by 2030, automation and AI could reduce the workforce demand by 20% to 25%, (with some predicting an even higher impact) amounting to a loss of 30 million to 40 million jobs. This disruption intensifies the debate over the necessity of a college education. While a degree has historically been associated with better employment prospects, the rapid pace of technological change demands adaptability and continuous learning. Alternative pathways, such as vocational training and certifications in emerging fields, are gaining traction as viable options.
To prepare for these shifts, access to affordable education and training is critical. Yet, barriers such as the rising cost of college and the burden of student debt limit opportunities for many U.S. citizens. As the nation grapples with the dual challenges of a polarized political landscape and a transforming economy, ensuring equitable access to education and reskilling programs will be essential for fostering a resilient workforce capable of meeting the demands of the future.
The Systemic Deterioration and Defunding of Public Schools
Considering the preparedness of students to enter secondary education compounding these challenges is the contentious issue of school choice, charter schools, and vouchers, a policy approach that has become a focal point in the battle over the future of American education. Proponents of school choice argue that it empowers parents, creates competition, and offers alternatives to failing public schools. Critics, however, contend that school choice programs exacerbate existing inequalities by diverting resources from public schools, potentially leaving them underfunded and struggling to serve their students.
The experience of Iowa City, Iowa, underscores the complex financial challenges that school choice programs can impose on public school districts. As more students opt for Education Savings Accounts (ESAs), which allocate public funds for private school tuition, public schools face declining enrollments and corresponding funding cuts. These funding losses and state-imposed spending caps force districts to make difficult decisions, such as eliminating teaching positions, increasing class sizes, delaying curriculum purchases, and cutting essential programs. While school choice programs offer options for some families, the Iowa City case highlights their unintended consequences, which can undermine the quality of education for all students.
A significant factor contributing to these challenges is the rigid structure of school funding in Iowa. Spending caps tied to enrollment mean that districts receive only $1,200 per student who accepts an ESA, far less than the per-pupil funding loss of $7,800. This disparity leaves districts like Iowa City unable to offset funding cuts through local tax increases, even if the community supports such measures. As a result, districts are left grappling with shrinking budgets and rising operational costs, despite serving fewer students. This inflexible funding design exacerbates the financial strain on public schools, particularly in the context of expanding ESA programs.
Adding to the difficulty is the lack of transparency and accountability in how these programs are administered. District officials in Iowa City were initially informed that 470 students within the district had accepted ESAs but received no clear data on how many were leaving public schools. This absence of critical information hindered efforts to plan for staffing, resources, and program allocations, leaving districts reactive rather than proactive in their budgeting. As the ESA program expands to include all K-12 students in Iowa by 2025-2026, this uncertainty will intensify, making long-term financial planning even more challenging.
The Iowa City example illustrates how poorly designed school choice programs can destabilize public education. Without foresight and adequate planning, these initiatives risk creating a volatile and inequitable environment for public schools, jeopardizing their ability to provide high-quality education and meet the needs of their communities. States like Iowa must address these systemic issues to ensure that school choice programs do not come at the expense of public education’s sustainability and accessibility.
The United States stands at a crossroads, grappling with the consequences of decades-long neglect of educational and workforce development. The ideological clashes within the MAGA movement mirror the larger societal debates over education access, affordability, and alignment with evolving labor market demands. While countries like Germany, Finland, and Singapore have invested in robust educational systems and aligned their policies with workforce needs, the U.S. has allowed financial barriers and political polarization to hinder progress.
As automation, AI, and global competition reshape the economy, the U.S. must prioritize policies that prepare its workforce for the challenges of the future. From expanding access to affordable education and reskilling programs to embracing global best practices, the nation has the tools to bridge its talent gap. However, success will require collective willpower, bipartisan cooperation, and a commitment to ensuring that every U.S. citizen can thrive in a rapidly changing world. Without these efforts, the U.S. risks falling behind as other nations surge ahead, armed with a skilled and adaptable workforce ready to lead the 21st century.
Sources
https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/maga-uncivil-war-elon-musk-vivek-ramaswamy-7kx8gxd5x
https://www.businessinsider.com/silicon-valley-bros-debating-maga-fans-over-h-1b-visas-2024-12
https://apnews.com/article/40b78d2b413aa473e31ca063e4dd5fa8
https://projects.cberdata.org/reports/SchoolSpendingChoice-20210611web.pdf
https://www.projects.cberdata.org/186/school-choice-and-state-spending-on-education-in-indiana
https://www.newsweek.com/h1b-immigration-visas-india-elon-musk-vivek-trump-2006308
https://www.edchoice.org/engage/analyzing-indianas-school-vouchers/
[https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/us/why-maga-turning-against-their-own-nikki-haley-and-laura-loomer-slam-elon-musk-vivek-ramaswamy-on-immigration/articleshow/116696511.cms](https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com










